
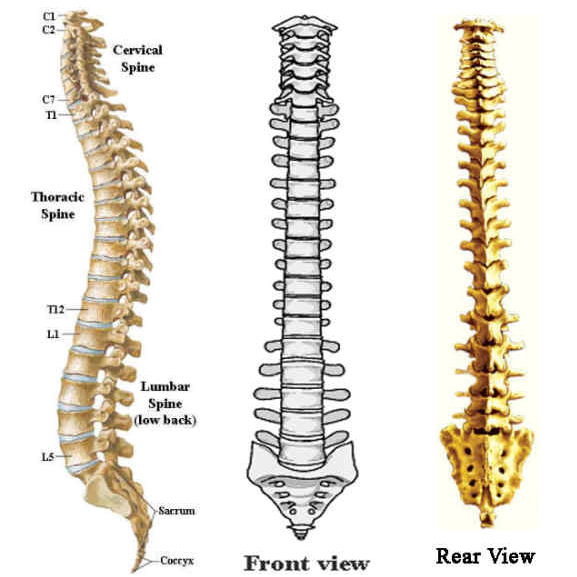
In quadrupeds the column is curved in a single arc (the highest portion occurring at the middle of the back), which functions somewhat like a bow spring in locomotion. The vertebral column is characterized by a variable number of curves. Humans have 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 fused sacral, and 3 to 5 fused caudal vertebrae (together called the coccyx). Whales show several specializations-the cervical vertebrae may be either much reduced or much increased in number, and the sacrum is missing. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae size rather than number account for the variations in neck length in different species. In turtles some vertebrae may be fused to the shell (carapace) in birds all but the cervical vertebrae are usually fused into a rigid structure, which lends support in flight. Snakes have the greatest number, all very similar in type. The numbers of vertebrae in each region and in total vary with the species. The atlas and axis vertebrae, the top two cervicals, form a freely movable joint with the skull. Crocodilians and lizards, birds, and mammals demonstrate five regions: (1) cervical, in the neck, (2) thoracic, in the chest, which articulates with the ribs, (3) lumbar, in the lower back, more robust than the other vertebrae, (4) sacral, often fused to form a sacrum, which articulates with the pelvic girdle, (5) caudal, in the tail.
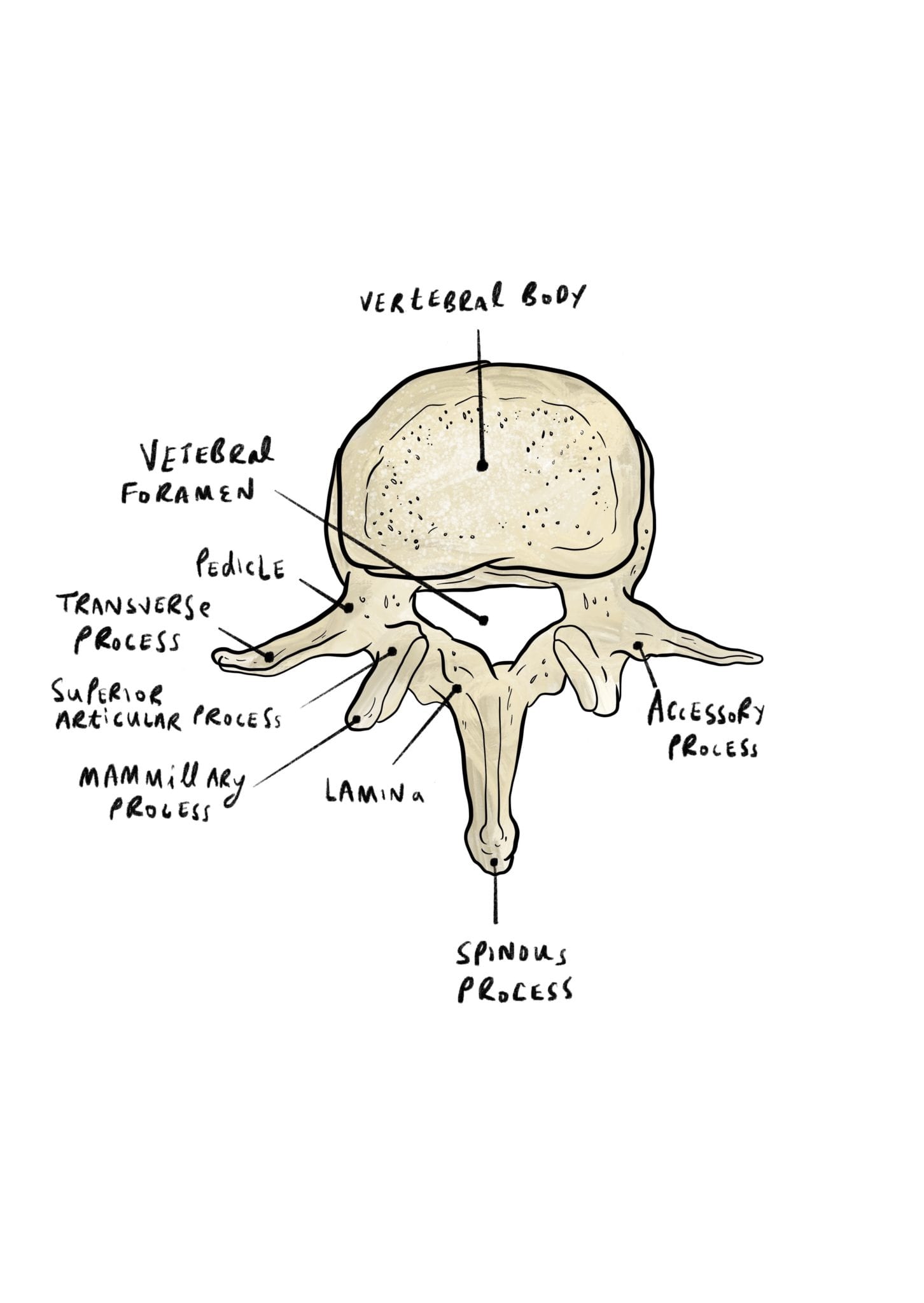
In primitive chordates the spinal cord is protected dorsally by segmented cartilages-these foreshadow the development of the neural arch of true vertebrae.įish have trunk and caudal (tail) vertebrae in land vertebrates with legs, the vertebral column becomes further subdivided into regions in which the vertebrae have different shapes and functions. The notochord appears in the embryos of all vertebrates in the space later occupied by the vertebral bodies-in some fish it remains throughout life, surrounded by spool-shaped centrums in other vertebrates it is lost in the developed animal. In primitive chordates (e.g., amphioxus, lampreys) a rodlike structure, the notochord, stiffens the body and helps protect the overlying spinal cord. Vertebrae in lower vertebrates are more complex, and the relationships of their parts to those of higher animals are often unclear. The centrums are separated by cartilaginous intervertebral disks, which help cushion shock in locomotion.Ībout how many bones do newborn humans have? What is the smallest bone in the human body? From mandibles and teeth to phalanges and spines, test your knowledge of bones in this quiz. Together the centrum and neural arch surround an opening, the vertebral foramen, through which the spinal cord passes.
SPINE ANATOMY SERIES
The arch extends a spinous process (projection) downward and backward that may be felt as a series of bumps down the back, and two transverse processes, one to either side, which provide attachment for muscles and ligaments. In humans an additional function is to transmit body weight in walking and standing.Įach vertebra, in higher vertebrates, consists of a ventral body, or centrum, surmounted by a Y-shaped neural arch. The major function of the vertebral column is protection of the spinal cord it also provides stiffening for the body and attachment for the pectoral and pelvic girdles and many muscles. Vertebral column, also called spinal column, spine, or backbone, in vertebrate animals, the flexible column extending from neck to tail, made of a series of bones, the vertebrae.
SPINE ANATOMY HOW TO


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
